
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome (BBS) is a rare genetic disorder with highly variable symptoms which may include retinal degeneration. BBS has a low prevalence in the population, affecting less than 1 in 100,000 people. Patients with BBS can experience problems with obesity, specifically with fat deposition along the abdomen, and they often suffer from intellectual impairments.
The Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 5 (BBS5) gene, located on human chromosome 2q31.1, is about 27kb in length and has 12 exons. Its encoded BBS5 protein consists of 341 amino acid residues and mediates binding to phospholipids, especially phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P), in vivo. In addition, BBS5 protein together with BBS1, BBS2, BBS4, BBS7, BBS8, BBS9 and BBS18 proteins form a heterooctameric protein complex, BBSome, which plays a key role in primary cilia homeostasis. Abnormalities in the BBSome can lead to severe Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS).
The BBSome complex is thought to function as a coat complex required for sorting of specific membrane proteins to the primary cilia. The BBSome complex is required for ciliogenesis but is dispensable for centriolar satellite function. This ciliogenic function is mediated in part by the Rab8 GDP/GTP exchange factor, which localizes to the basal body and contacts the BBSome. Rab8(GTP) enters the primary cilium and promotes extension of the ciliary membrane. Firstly, the BBSome associates with the ciliary membrane and binds to RAB3IP/Rabin8, the guanosyl exchange factor (GEF) for Rab8, and then the Rab8-GTP localizes to the cilium and promotes docking and fusion of carrier vesicles to the base of the ciliary membrane. The BBSome complex, together with the LTZL1, controls smoothened (SMO) ciliary trafficking and contributes to the sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathway regulation. The BBSome is the major effector of Arl6 in retinal extracts. Thus, Arl6 is specifically required for BBSome localization to cilia but not for BBSome assembly [1].

In the 1880s, a family with retinitis pigmentosa, obesity, and intellectual impairment was described by doctors Laurence and Moon. The affected family members later went on to develop a spastic paraparesis, with their disorder ultimately being named Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS). BBS is a rare autosomal recessive ciliopathy; Genes associated with BBS are listed in Table 1. Mutations in BBS1 and BBS10 account for the majority of genotypes (~51 and ~20%, respectively) in Northern Europe and North America. Bardet Biedl syndrome proteins localize to the primary cilium/basal body complex, a ubiquitously expressed highly evolutionarily conserved organelle functioning primarily for cell-to-cell signaling. The genes that cause BBS can also cause other additional ciliopathies, with the classic example being CEP290, which can cause Joubert syndrome, Leber congenital amaurosis, Meckel syndrome, and Senior-Loken syndrome.
| BBS type | Gene name |
|---|---|
| BBS1 | BBS1 |
| BBS2 | BBS2 |
| BBS3 | ARL6 |
| BBS4 | BBS4 |
| BBS5 | BBS5 |
| BBS6 | MKKS |
| BBS7 | BBS7 |
| BBS8 | TTC8 |
| BBS9 | BBS9 |
| BBS10 | BBS10 |
| BBS11 | TRIM32 |
| BBS12 | BBS12 |
| BBS13 | MKS1 |
| BBS14 | CEP290 |
| BBS15 | WDPCP |
| BBS16 | SDCCA8 |
| BBS17 | LZTFL1 |
| BBS18 | BBIP1 |
| BBS19 | IFT27 |
| BBS20 | IFT172 |
| BBS21 | C8orf37 |
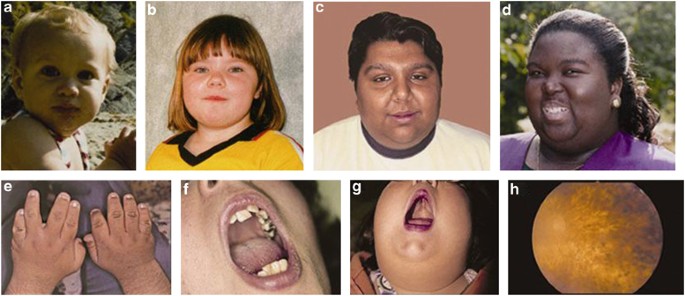
The cardinal features of BBS are truncal obesity, intellectual impairment, renal anomalies, brachydactyly, retinal degeneration, and hypogenitalism. Of note, many people with BBS also have problems with their sense of smell. Patients with BBS have a decreased ability to sense smells due to a change in the size of a brain center called the “olfactory bulb”. This is a relatively mild problem but may impact safety if people are unable to sense, for example, a gas leak from the stove. Problems with fertility arise in both men and women. Pregnant women with BBS should be followed closely by obstetricians that are well trained in dealing with high-risk pregnancies.
- Jin H, White SR, Shida T, Schulz S, Aguiar M, Gygi SP, Bazan JF, Nachury MV. The conserved Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins assemble a coat that traffics membrane proteins to cilia. Cell. 2010 Jun 25;141(7):1208-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.05.015. PMID: 20603001; PMCID: PMC2898735.
- https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8N3I7
- Forsythe E, Kenny J, Bacchelli C, Beales PL. Managing Bardet-Biedl Syndrome-Now and in the Future. Front Pediatr. 2018 Feb 13;6:23. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00023. PMID: 29487844; PMCID: PMC5816783.




